Frequently Asked Questions For ABB Residual Current Devices (RCDs)
ABB Low Voltage 12th Dec 2022
 Which is the working voltage range of an RCD?
Which is the working voltage range of an RCD?According to the product standards for RCDs, these devices have to be equipped with a test device to simulate the passing through the detecting device of a residual current in order to allow a periodic testing of the ability of the residual current device to operate. The operating voltage of the test button identifies the working voltage of the RCD: Ut range is the real operating range of an RCD because the device has to be installed in way it’s possible to test it using test push button. In order to properly evaluate the functioning of the test circuit, it must be considered the wiring of internal test circuit. In the technical catalogue, for each RCD range you can find the Ut voltage range and the position of the internal test circuit; here follow an example for F200 RCCB range.

Maximum and minimum operating voltage of F 200 RCCB standard test button
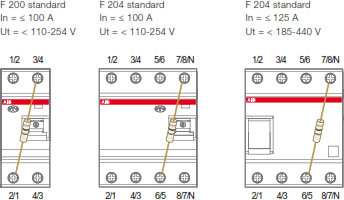
With this information, referring to the F202 standard it is clear indicated that the device will properly work if it is supplied between 110 and 254V. Considering an F204 standard (≤ 100A) the device will properly work if it is supplied between 110 and 254V within the terminal 5/6 and 7/8/N. The rated voltage Un is the voltage reference given by the product standards for the test sequence prescribed by these standards.
Is it possible to use a F204 RCCB in a 3 phase system without neutral?
The internal circuit of test button of the RCCB F204 is wired inside the device between terminals 5/6 and 7/8/N as shown in the picture and has been sized for an operating voltage between 110 and 254 V.
If the circuit is supplied with a concatenate voltage higher than 254 V, as in the typical case of 3 phase network with concatenate voltage (phase-phase) of 400 V, it is not possible to use these RCDs wiring only the phases because the circuit of the test button will not be supplied.
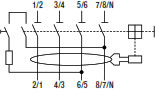
Also it is not possible to use the RCCBs shifting the cables of one pole (phases on terminals 3/4 - 5/6 and 7/8/N) because the circuit of the test button will be supplied at 400 V and it will give a not exact information about functionality.
The solution is to connect the three phases to the terminals 1/2, 3/4, 5/6 and to add an external resistance between the terminals no. 4/3 and 8/7.
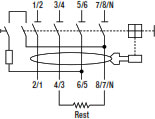
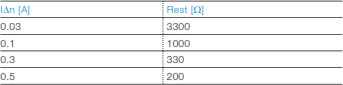
The value of the external resistance (?) depends on the I?n of the selected RCCB, as shown in the table:
Another solution for a 3P system without neutral is to use the F204 with neutral on the left side. In this case the test circuit is wired between terminals 3/4 and 5/6 and it is possible to connect the three phases on terminals 1/2, 3/4 and 5/6 without the need to add an external resistance:
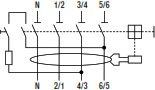
This is the maximum and minimum operating voltage of F200 RCCB with neutral on the left
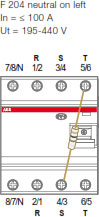
Which are the possible wiring configurations for a 4P RCCB of the F200 range?

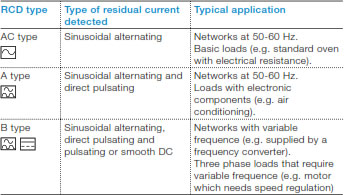
Which is the difference between AC, A and B type RCDs and which are typical applications for different type of RCDs?
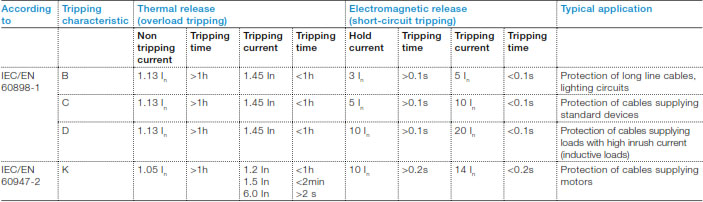
Considering an RCBO, which is the right tripping curve to be selected depending on the application?
Which is the difference between direct contacts and indirect contacts?

A direct contact refers to a person coming into contact with live parts or conductors that are normally live: the main protection against direct contacts is the physical prevention of contact with live parts by means of barriers, insulation, inaccessibility, etc.

An indirect contact refers to a person coming into contact with an exposed conductive part which is not normally alive, but has become alive accidentally (due to insulation failure or some other cause). The protection against indirect contacts is mainly realized by disconnection of the supply, by means of a residual current device. RCDs of high sensitivity (I?n ≤ 30mA) are able to provide both protection against indirect contact hazards and the additional protection against the dangers of direct contact.
Why 30mA is the preferred value for Idn?
The IEC publication 60479-1 "Basic safety publication on the effects of current on human beings and livestock" provides basic guidance on the effects of shock current on human beings and livestock, for use in the establishment of electrical safety requirements. For a given current path through the human body, the danger to persons depends mainly on the magnitude and duration of the current flow.

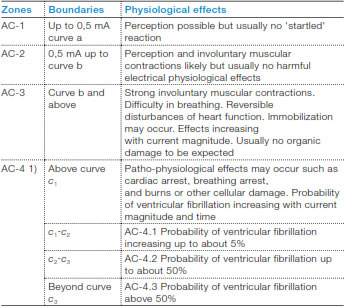
This publication defines 4 zones considering the hazards of electric shock on human body depending on currentmagnitude/time duration.
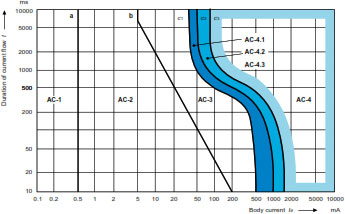
The more dangerous area is the AC-4 where physical damages could occur to human body. When a current higher than 30 mA passes through a part of a human body, there is serious danger for people if the current is not interrupted in a very short time:
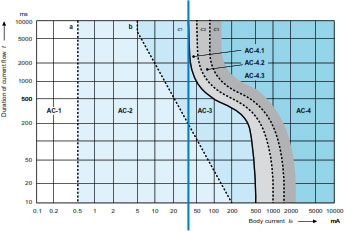
It‘s a common statement that in order to protect people from direct contact an high sensitive RCD is strictly recommended. According to IEC publication 60364-4-41 (Low-voltage electrical installations – Part 4-41: Protection for safety – Protection against electric shock) an RCD suitable for protection against Direct Contact has to have its trip threshold set at 30 mA for AC current. These devices, used to disconnect the power supply automatically, operate as fast to prevent injury to, or death by electrocution, of a normally healthy human. In fact it detecs any earth leakage current which may circulate through a person, and which does not loop back to the source via the live conductors PE.
How to coordinate MCBs and RCDs speaking about short circuit?

Rated making and breaking capacity (Im) is the capacity of the RCCB to make, to carry for a specified time and to break short-circuit currents. Rated residual making and breaking capacity (I?m) is the capacity of the RCCB to make, to carry for a specified time and to break residual short-circuit currents. These values are laser printed in front of the RCCB and written in the technical catalogue.
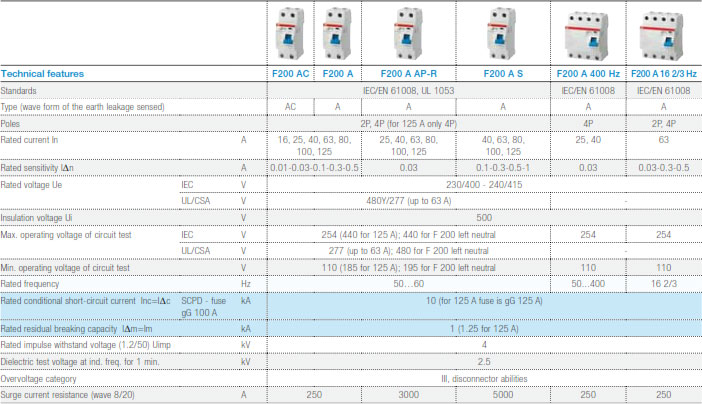
Rated conditional short-circuit current (Inc) is the value of current which a RCCB, protected by a Short Circuit Protection Device, can withstand under specified conditions (without losing its functions).
Rated conditional residual short-circuit current (Idc) is the value of residual current which an RCCB, protected by a Short Circuit Protection Device, can withstand under specified conditions (without losing its functions). Inc and I?c are assigned by the manufacturer.
Inc/I?c according IEC/EN 61008 is related to a Short Circuit Protection Device (SCPD). Typically for SCPD it is considered a fuse due to the fact the breaking capacity and limitation of a fuse is not linked to a brand so it is possibile to coordinate the RCDs with fuse on the market, independently from its brand. The coordination between RCDs and MCBs has to be tested in laboratory because if you are using an RCCB in combination with MCB you must verify that the Short Circuit Protection Device used protects RCD from the effects of high current that arise under short-circuit conditions.

The product standard IEC/EN 61008 provides some tests to verify the behaviour of RCCB in short-circuit conditions The values of Inc and I?c have to be related to the type of SCPD to prove these values and its rated current: RCCBs F200 series have been tested with an SCPD (a fuse) with rated current 100A (Inc=10kA) and this indication is in front of the F200.
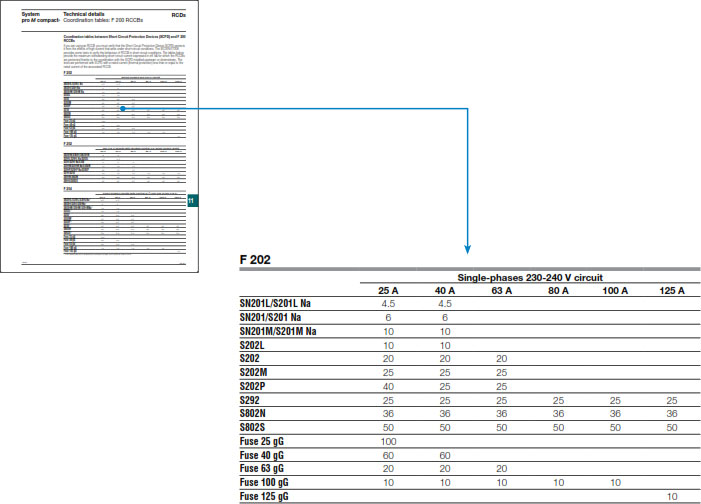
What does ABB provide in addition? Coordination tables between MCBs and F200 RCCBs. ABB supply tables with the maximum short-circuit current (kA) for which the RCCBs results protected thanks to the coordination with the MCBs installed upstream or downstream. The tests have been performed with SCPD with a rated current (thermal protection) less than or equal to the rated current of the associated RCCB. You can find the most updated version of these tables on the technical details in the System pro M compact catalogue!
Which is the difference between UL Listed (UL) and UL recognized (UR) products? F200 is UL or UR certified?

The key difference is that a UL Listed product is complete and can be used as is by the purchaser. Products bearing the UL Listing Mark are usually either complete appliances. A UL recognized component is a component to be used in the construction of some other product. Comparing UL Listed devices and UL Recognized components is like comparing a computer and a RAM (random access memory). A computer is a finished product, and the RAM is a necessary component. However, not every RAM is compatible with every computer. This applies also for UL Recognized Components, which will not be compatible with all end-product equipment applications. F200 RCCBs are UL Recognized components (according to UL 1053 standard) as they are only intended for installation in end products (switchboard, machine, etc) whose safety is evaluated by UL separately.
12th Dec 2022


